Overview to Object-Oriented Programming in Python
Python is one of the most popular high level interpreted programming language which is being used in many technologies, like web apps, mobile apps, machine learning, etc., as every thing is dynamic and simple in python. Due to the huge popularity of Python, it'll be very advantageous if you know OOPs in Python, as OOPs becomes very useful and contributive in solving real-life problems very efficiently. In this blog, we'll be learning/revising, Class, Objects and many other Object-Oriented Programming concepts in Python.
Hey coder, this blog will be basically a python cheat sheet for you. Before heading to Object-Oriented Programming in Python, let's first see what are the concepts that falls in the vital segment of OOPs. Afterwards, we will also see some example on Object-Oriented Programming in python.
Topic that are essential to know while learning in OOPs are:
- Class
- Object
- Encapsulation
- Polymorphism
- Inheritance
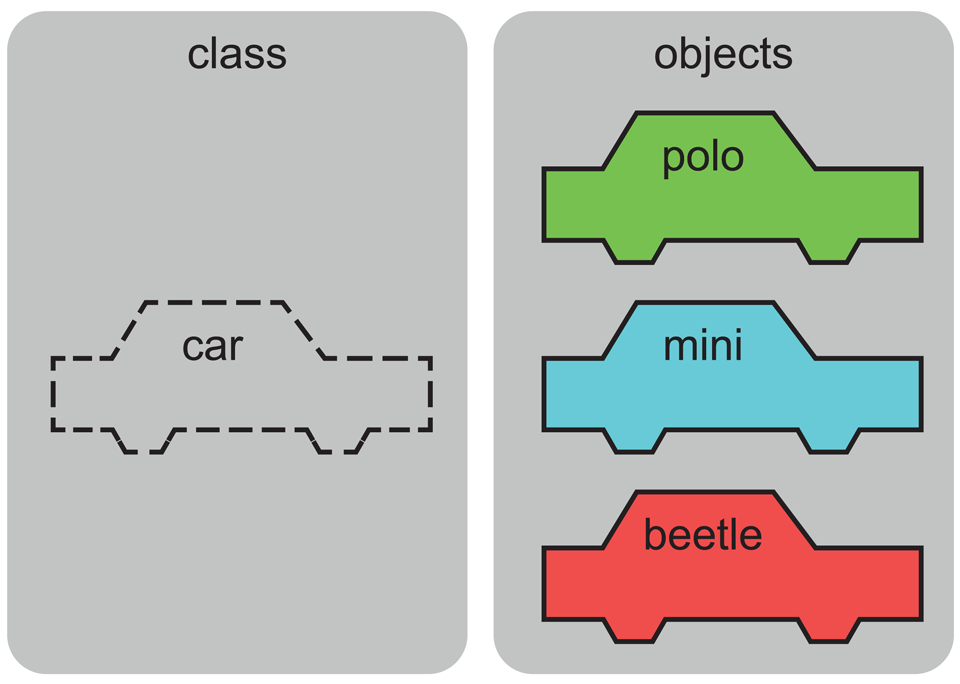
Class in Python
A Class is nothing but a prototype or a blueprint that helps in the creation of objects with specific of instances/methods/behaviours. A class is not a physical entity, on the contrary, it is a imaginary system/entity having variables and functions. It is helpful specially when you want to produce a lot objects/instances that have some behiours by the time of creation. Let's see an real life example, suppose you have to count cars in your city. Now, you already know, not all cars in your city will have same specification, so it'll be difficult to even verify whether an object (which might be a car) is a car or not, if you start your counting work by taking any particular car as the referential object. The task will be complited iff all cars in your city are same, otherwise how would you even know which object is a car and which object are not. Even if you know that configuring properties of that referential car (object), you can define a car, but the thing is, how you could add or remove a property from an object?
So, this can be a situation wherein you can need the classes. As they are the blueprint, so you can add/remove/customize the methods or attributes, you can easily do that.
In python, you can create a class of by using the keyword class. You can access the methods and attributes of a class in python using a . (dot) operator.
Object in Python
An Object is an occurrence of a Class. A class resembles an outline while an occasion is a duplicate of the class with real qualities. Python is object arranged programming language which weight on objects for example it basically stress on capacities. Objects are fundamentally an embodiment of information factors and strategies following up on that information into a solitary element.
Instance characterizing address memory allotment fundamental for putting away the real information of factors. Each time when you make an object of class the duplicate of every information factors characterized in that class is made. In straightforward language we can express that each object of a class has its own duplicate of information individuals characterized in that class.
E.g. object_obj = MyClass()
Encapsulation in Python
An Encapsulation is one of the essential ideas in object-oriented programming (OOP). It portrays wrapping information and the techniques that work on information inside one unit. This puts limitations on getting to factors and strategies straightforwardly and can forestall the unintentional change of information. To forestall unintentional change, an article's variable must be changed by an item's technique. Those sorts of factors are known as private variable. A class is an illustration of epitome as it exemplifies every one of the information that is part works, factors, and so on.
Note: Python's private and protected part can be gotten to outside the class through
Polymorphism in Python
Polymorphism means multiple forms.In python we can observe a similar administrator or capacity taking various structures. It likewise helpful in making various classes which will have class strategies with same name. That aides in re utilizing a great deal of code and diminishes code intricacy. Polymorphism is additionally connected to legacy as we will find in certain models beneath.
- Polymorphism in in-built functions
- Polymorphism in user-defined methods
- Polymorphism in operators
We can likewise see that distinctive python capacities can take contributions of various kinds and afterward process them in an unexpected way. At the point when we supply a string worth to len() it includes each letter in it. However, on the off chance that we five tuple or a word reference as an info, it processes them in an unexpected way.
We can make techniques with same name yet wrapped under various class names. So we can continue to call a similar strategy with various class name pre-fixed to get distinctive outcome.
The + administrator can take two data sources and give us the outcome relying upon what the data sources are. In the beneath models we can perceive how the whole number information sources yield a whole number and on the off chance that one of the information is float then the outcome turns into a float. Likewise for strings, they absolutely get linked. This happens consequently in view of the way the + administrator is made in python.
Inheritance in Python
InheritanceInheritance is a significant part of the article arranged worldview. It gives code reusability to the program since we can utilize a current class to make another class as opposed to making it without any preparation.
In Inheritance, the youngster class procures the properties and can get to every one of the information individuals and capacities characterized in the parent class. A youngster class can likewise give its particular execution to the elements of the parent class. In this part of the instructional exercise, we will examine the inheritance exhaustively. In python, a determined class can acquire base class simply by referencing the base in the section after the inferred class name.
Note: A class can inherit multiple classes by mentioning all of them inside the bracket.
This was a brief overview of OOPs in Python. This would help you get a basic idea about the OOPs concept. We'll be publishing a detailed blog on each of the topic of Object-Oriented Programming using Python3, Java, and C++.
Keep learning, keep practicing.
Until then, Happy Coding.







No comments: